What is PETG? Everything about the versatile filament
In this article I introduce the 3D printer filament PETG, or PETG filament, which has become a popular material for 3D printers(ready-to-use printers/3Dprinter kits) in recent years.
I discuss the differences to PET, show the advantages and disadvantages, and give tips on processing and post-processing. After that, some manufacturers or distributors of PETG filament are listed.
After reading this article, you will have a rock-solid basic knowledge of this very versatile plastic.
Where can I buy PETG filament?
Here is a first list of selected filament from various manufacturers:
* Stand: 2024-04-21 / Bilder: Amazon API
If this selection is not enough for you, feel free to visit the following page for more:
Buy PETG Filament – Current Best Sellers
What is PETG?
PETG is the short version of the chemically correct name of polyethylene terephthalate. Known as a conventional PET material in bottle form, it provides better processing properties with a glycol modification. This raw material guarantees low viscosity in production.
This means that the material becomes liquid rather than viscous after heating. It also has a high level of transparency. A milky, almost transparent surface can be achieved by varying the printing speed and temperature.
What is PET?
In our modern environment, PET(polyethylene terephthalate) is one of the most widely used plastics in the world. PET is not only used in the food industry, but in almost all areas of life. The polyester plastic is made from 100 percent natural gas or petroleum and is recycled to a high degree. Primary products include beverage bottles as well as bags, ski jackets and, increasingly, soccer jerseys.

What is the difference between PETG and PET?
Both materials are used in a variety of consumer products via detours. PET often in the conventional production process, whereas PETG filament can combine enormous advantages in 3D printing. The combination with glass fibers or biochemical components provide individual solutions in different industries.
PETG base material is suitable in its processing for both injection molding and 3D printing, its decisive advantage in direct comparison with PET is durability. While heating makes PET products brittle and cloudy in the long term, PETG raw material behaves more stably despite permanent use. Neither does it become fragile over time, nor does the layer adhesion suffer. The addition of glycol produces an impact-resistant product that can be sterilized without any loss of quality and is therefore also used in medical technology.
What are the advantages of PETG filament for 3D printing?
PETG clearly owes its continuously stable and rapid processing capability to its very good surface properties. Optimal layer adhesion and minimal deviations in warping or shrinking make processing PETG filament in 3D printing with minimal difficulties. The 3D printed objects shrink by only 0.5 percent after cooling. This makes it possible to achieve high reproducibility of results with consistent printer settings.
PETG filament combines various properties that are synonymous with efficient processes in 3D printing, namely durability, robustness, temperature resistance and the ability to print cost-effectively or quickly with the base material.
What are the disadvantages of PETG filament for 3D printing?
In direct comparison with other printing materials, PETG filament performs very well. There are very few obvious drawbacks to 3D printing, but the material is not 100 percent UV resistant. It also suffers scratch marks more quickly. Apart from isolated mechanical differences, PETG makes for exceptionally straightforward use in 3D printing.
Is PETG filament food safe?
Although the raw material of PETG filament is sourced from a wide variety of countries, they all share a quality label – they are food safe and can be classified as harmless.
Detailed data sheets from the manufacturers and precise article descriptions help to obtain exact information on the basic material in every case. These should be checked or requested by mail before an appropriate application.
The guarantee of producing food-safe consumer products enables PETG filament to be used in such a wide range of applications that their use seems almost endless.
What are some examples of applications for PETG filament in 3D printing?
Almost perfect material for DIY projects, concept and functional models.
Since the simple processing method is very unproblematic, its use in almost all projects is a cost-effective and logical decision. In professional terms, functional models can be printed and mechanically examined at many stages of development. They provide an opportunity to incorporate experience and ideas directly on the design to move to the next phase of planning.
PETG settings: Which values should I take?
This section presents the print settings for PETG. First, we will start with the printing temperature and then go into the topics of print bed/heating bed as well as printing speed.
What is the best printing temperature for PETG?
A temperature of 220°C to 250°C is recommended by many manufacturers. However, the ideal setting can vary not only from manufacturer to manufacturer, but also within the manufacturer. This is due to the various additional materials needed to achieve certain colors.
That is:
Color yellow from manufacturer A may require a different temperature setting than color red from manufacturer A.
As with all filaments, the following applies to a good start for 3D printing:
If the correct melting temperature is not reached and the filament is not extruded liquid, the temperature must logically be increased slightly. The perfect print run is a mix of the right temperature and the right speed. Lower printing speeds are recommended for the start in order to better assess the material. If good adhesion to the print bed and good layer adhesion are achieved, the speed can be increased.
Is a heated print bed (heatbed) required for 3D printing with PETG filament?
No, 3D printing is basically possible without a heated print bed. This depends primarily on the print substrate used. However, if larger components are to be printed and adhesion to the print substrate is not optimal, temperatures of around 60°C should be used according to the manufacturer's specifications. Here again, it is important to find the optimum values for your own material in combination with your own 3D printer.
In our own trials with different suppliers, good results were also achieved with a bed temperature of 65°C/75°C or even 85°C. In combination with the Pertinax pressure pad, for example, 65°C is a good initial value.

What printing speed is recommended?
As already described above, slow printing is recommended especially for the first handling of PETG and also other filament types. If your 3D printer's print speed is set to 60 mm/s, I would start with 45 mm/s first.
In most slicers, the speed of the first layer is also coupled with this and will also decrease. This is not a bad thing, however, because it also reduces the risk of warping.
Is the result satisfactory? Then you can increase the speed and test again.
What is the best way to store PETG filament?
PETG is actually resistant to many influences, but storage should be in a dry room. Too much humidity can lead to changes in the material and end up causing faulty 3D prints. Additional packaging – for example, in a plastic box with a silicate bag – can keep additional moisture from entering the packaging.
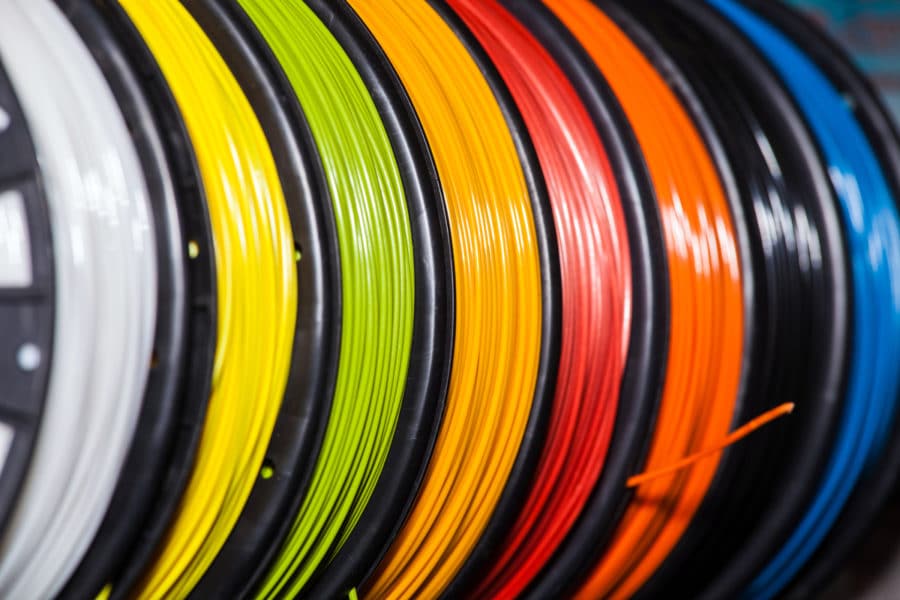
In which colors is PETG filament available?
Within the color spectrum, PETG offers a wide range of different colors. The selection spans the same range available with other materials such as PLA in 3D printing. There is a suitable filament for every color choice.
* Stand: 2024-04-21 / Bilder: Amazon API
Can PETG filament be glued?
Post-gluing 3D prints is one of the most effective post-processing options. Depending on the size and number of different assemblies, gluing together is an extremely useful method when you want to create models that have more volume than the 3D printer itself. With just a few components, it is possible to create a powerful connection between the individual parts. Basically, several types of adhesives are suitable for achieving optimum results. Cyanoacrylate adhesive, for example, ensures perfect hold in seconds.
Procedure: The adhesive is carefully applied along the seam as well as distributed at central points. To achieve uniform adhesion, it is advantageous to work from the center outwards at regular intervals. Excess adhesive is simply removed with a paper towel, but this should be done immediately after joining, as Power Adhesive cures very quickly.
Conventional epoxy adhesive is used to join FDM components. Its two components are mixed and then applied with the help of brushes or dispensers. Various techniques are used for application. The individual model parts are stabilized with rubber bands, clamps or their own assembly devices until the adhesive has cured. At room temperature, complete cure cycles can take one to five days, but this time can be drastically shortened by applying a hot cure or using accelerators.
Unlike epoxy, cyanoacrylate is faster curing and ideal for small repairs that are subject to light use. However, its resistance to higher temperatures, solvents and chemicals is rather poor. Thus more suitable for concept models or simple functional prototypes.
Can PETG filament be smoothed like ABS with acetone or similar?
Great final results are most likely to be achieved with sanding or clear coat applied afterwards. Epoxy resin ensures a glossy and high-quality appearing surface structure of the finished printed object. What works great with ABS using acetone is not a viable solution when using PETG filament. Since the material is largely immune to acetone and commonly used solvents, this post-treatment method provides no benefit. Thus, 3D printed models made of PETG filament do not get a smoother surface.



